There are many arguments about which diet is best for you.
Nevertheless, health and wellness communities agree that diets emphasizing fresh, whole ingredients and minimizing processed foods are superior for overall wellness. There are many types of plant-based diets.
The whole-foods, plant-based diet does just that.
Nonetheless, the basic principles of a whole-foods, plant-based diet are as follows:
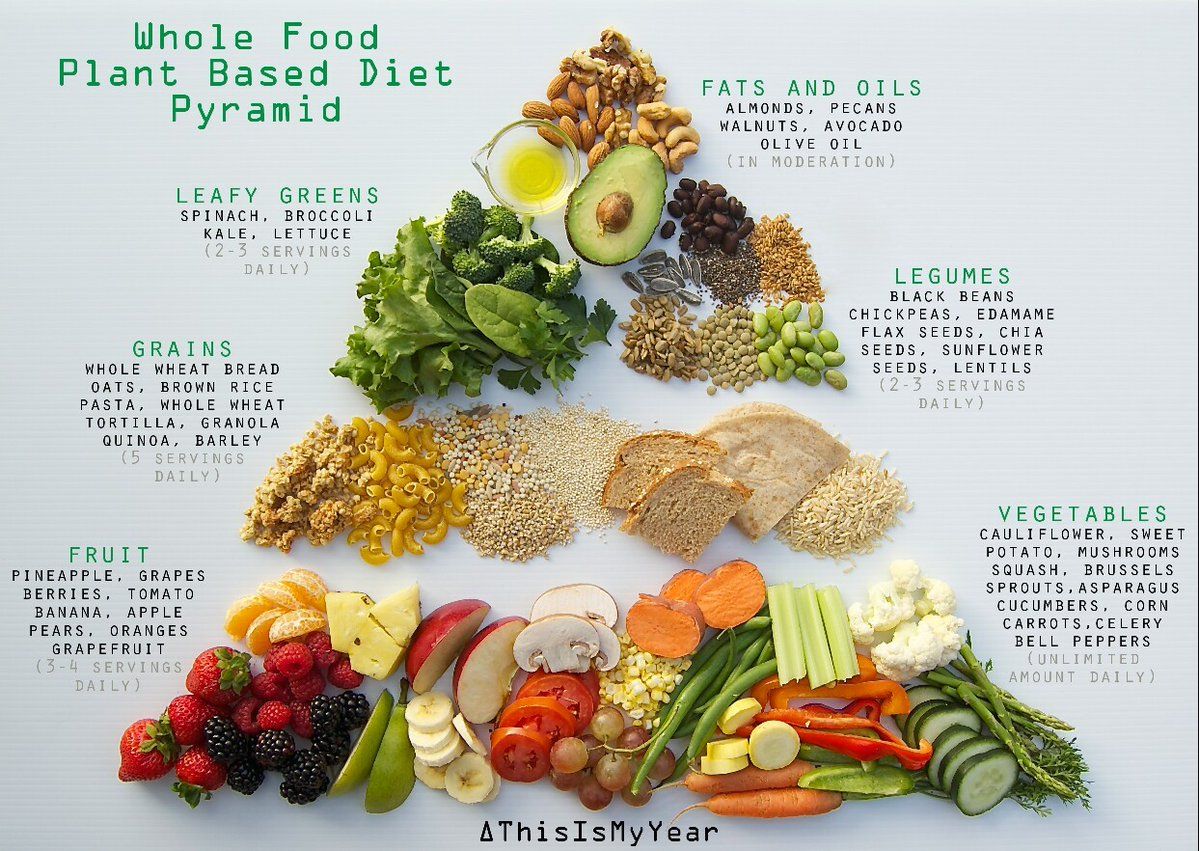
- Emphasizes whole, minimally processed foods.
- avoids animal products (Milk, Dairy-based food products, Egg, Fish, Meat).
- Focuses on plants, including vegetables, fruits, whole grains (unpolished), legumes, seeds, and nuts, which should make up the majority of what you eat.
- Excludes refined foods, like added refined sugars, white flour, and oils.
- Pays special attention to food quality, with many proponents of the WFPB diet promoting locally sourced, organic food whenever possible.
- For these reasons, this diet is often confused with vegan or vegetarian diets. Yet although similar in some ways, these diets are not the same.
People who follow vegan diets abstain from consuming any animal products, including dairy, meat, poultry, seafood, eggs, and honey. Vegetarians exclude all meat and poultry from their diets, but some vegetarians eat eggs, seafood or dairy.
The WFPB diet, on the other hand, is more flexible. Followers eat mostly plants, but animal products aren’t off-limits.
While one person following a WFPB diet may eat no animal products, another may eat small amounts of eggs, poultry, seafood, meat or dairy.
SUMMARY
The whole-foods, plant-based diet emphasizes plant-based foods while avoiding animal products and processed items such as refined sugar, white flour, vegetable oils.
